Food Web Peacock Food Chain
Most people call them peacocks but that s only.
Food web peacock food chain. Some insects eat other insects so in that. They eat grains vegetables berries seeds and plants and also small animals such as insects worms and even small mammals like shrews. They make their own organic matter from nutrients co2 and light photosynthesis. It is an omnivore and eats plant matter insects and small arthropods.
Peacocks are fairly omnivorous. Food webs can support food chains that are either too long and complicated or too short. Peacocks peafowl get their food mostly on the ground like small snakes lizards frogs bugs flower petals bananas seeds grains and left out food by humans. This is a primary difference between a food web and a food chain.
The concept of a food web is credited to charles elton who introduced it in his 1927 book animal ecology. Corn wheat and other grains are a common food source for peacocks. These are terrestrial plants or aquatic ones algae phytoplankton. Cantaloupe and watermelon for instance have large seeds that contain nutrients necessary to a peacock s diet.
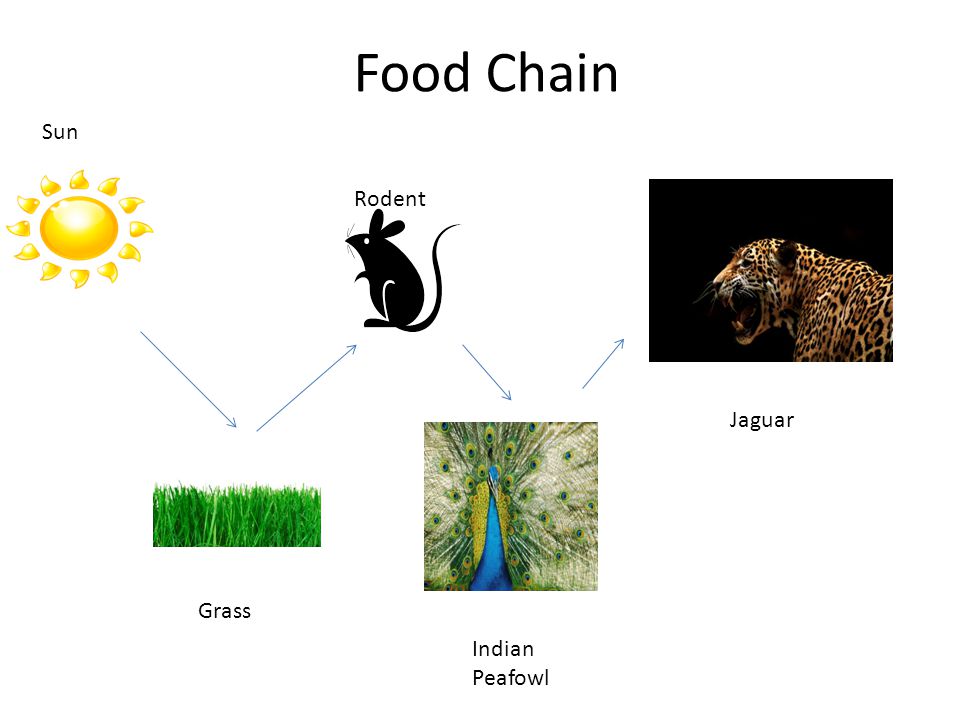
A peacock peafowl like many other birds is a first and second order consumer. Peacock food chain food chain of a peacock. For example in a desert food web you d start 1 arrow at the grass and connect it to the grasshoppers. A male peacock s feathers can reach up to 6 ft.
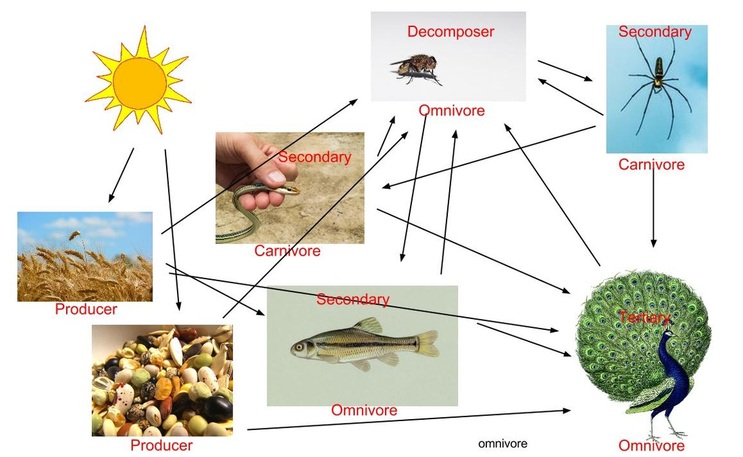
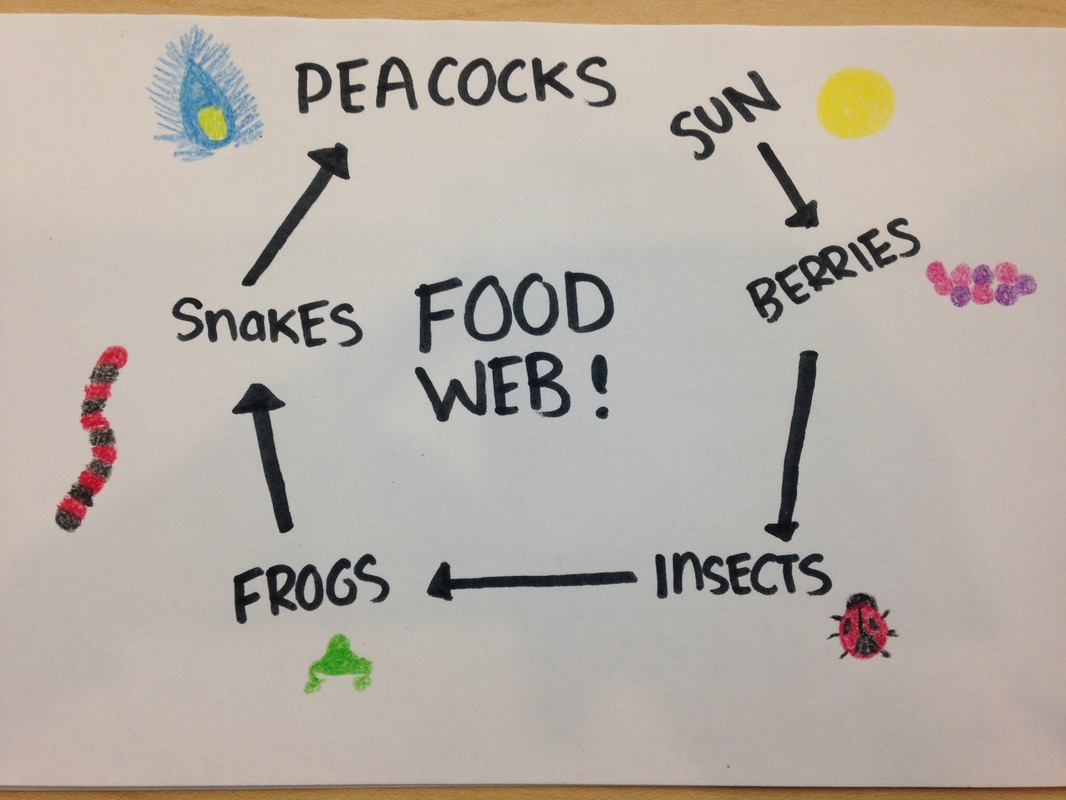
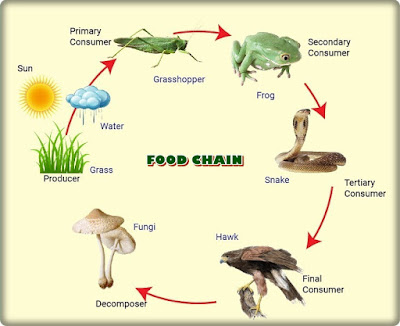
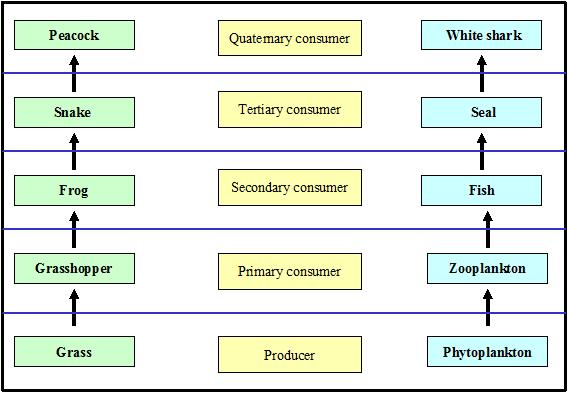
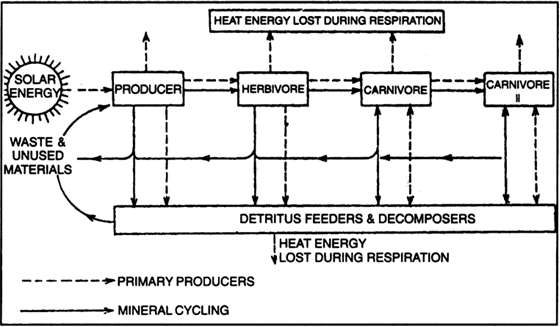
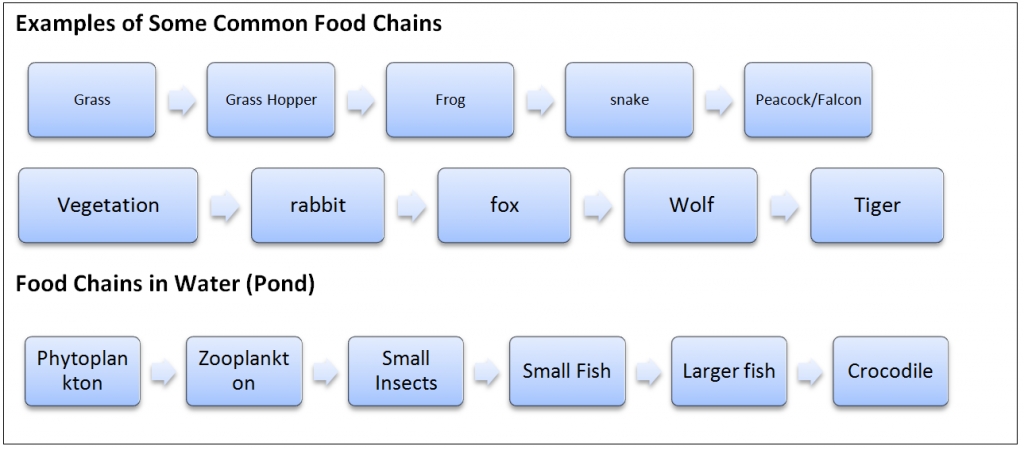
A food chain is an organized series of living things linked together by an alimentary food related relationship. Peacocks in nature have a. Food webs connect many different food chains and many different trophic levels. At the base of such a chain one finds the producers.
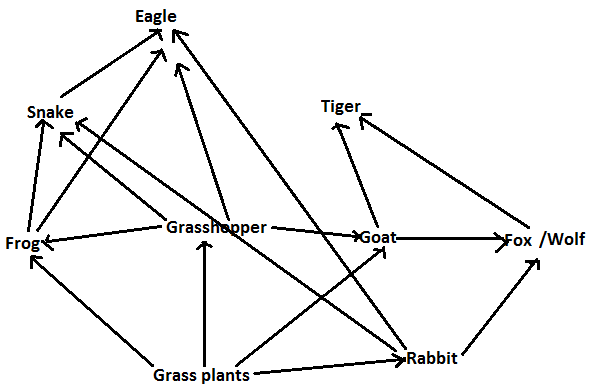
You d start another arrow at the grass and connect it to the rats too. According to the biological definition food chain is the feeding relationship that transfers energy from one trophic level to another in an ecosystem. A food web is a bit more chaotic in that it can show multiple different arrows between creatures. Animals draw the energy needed for survival from their food.
The interconnectedness of how organisms are involved in energy transfer within an ecosystem is vital to understanding food webs and how they apply to real world science. A food web can be described as a who eats whom diagram that shows the complex feeding relationships in an ecosystem. In this food chain peacock occurs at the highest trophic level therefore peacock will have the maximum concentration of harmful chemical in its body.